A cell is the smallest unit of the human body. Many organs are made up of tissues, which in turn, are made up of minute cells present throughout the body. Within these cells takes place the process of cell division. To understand it well, know the main stages of the cell division that helps organisms in many different ways. To start with, Cell division plays different roles depending on the organisms.
For unicellular ones, it helps in reproduction; for multicellular ones, it counts for tissue growth and maintenance. Different cells mark the process of cell division in different forms. Skin cells shed and re originates, liver cells undergo regenerations after the injury, etc. Here are some of the stages of cell division that helps in the formation of multiple cells.
Types of Cell Division
The process of cell division takes place in the two main ways, including Mitosis and Meiosis. In Mitosis, the cells undergo division to take care of the repair and maintenance of the body. While in Meiosis, the cell division takes place to back firm the reproduction process.
During the process of cell division, the initiation takes place by the condensing of the DNA for the formation of rodlike chromosomes. In the process, the chromatids divide up into two daughter cells causing division of the nucleus as well. There are five main stages of cell division in Mitosis. Here are all of them quoted.
5 Stages of Cell Division in Mitosis
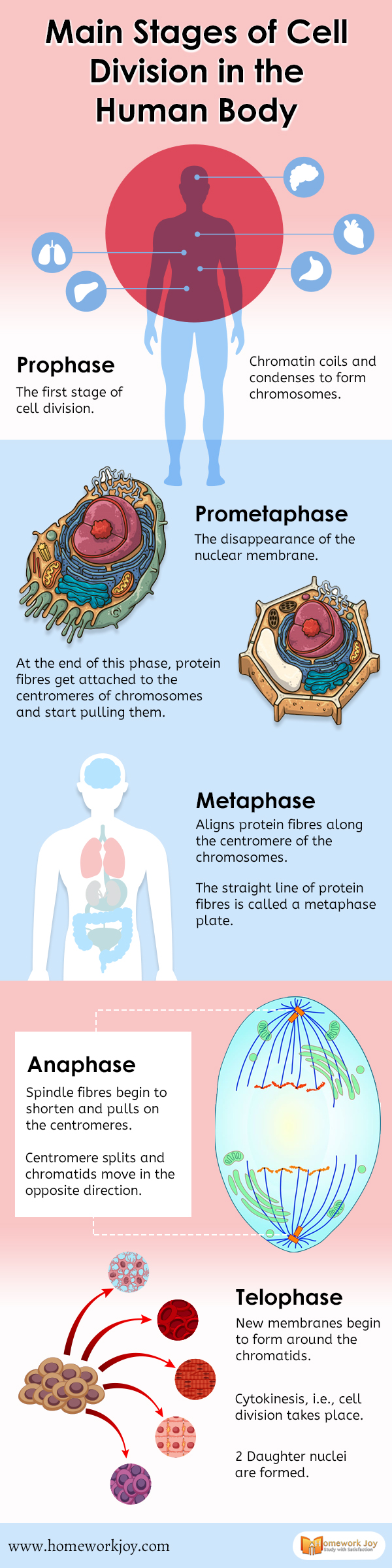
Prophase
- Prophase is the first stage of cell division. Mitosis begins with prophase, which occurs after the preparatory stage. The cells at this stage begin breaking down some structures for the preparation of other chromosomes.
- Chromatin coils and condenses to form chromosomes
- The nuclear envelope breaks down
- The centrosome starts movings towards the opposite poles
Prometaphase
- The disappearance of the nuclear membrane
- At the end of this phase, protein fibers get attached to the centromeres of chromosomes and start pulling them
- The chromosomes further continue to condense
- A network of cells called kinetochores appears at the centromere
- The spindle fibers continue to attach to the kinetochores
Metaphase
- Aligns protein fibers along the centromere of the chromosomes
- The straight line of protein fibers is called a metaphase plate
- The opposite sister chromatids come closer to and attach to the spindle fiber
Anaphase
- Spindle fibers begin to shorten and pulls on the centromeres
- Centromere splits and chromatids move in the opposite direction
- The spindle fiber also get the ability to elongate the cell
Telophase
- New membranes begin to form around the chromatids
- Cytokinesis, i.e., cell division takes place
- 2 Daughter nuclei are formed
Cytokinesis
- Formation of a cleavage furrow to separate the daughter cells: In the animal cell
- A cell plate is formed prior to the new wall to separate the daughter cells
These stages of the cell division help in the division of the cells to form daughter nuclei and look after the repair and maintenance.