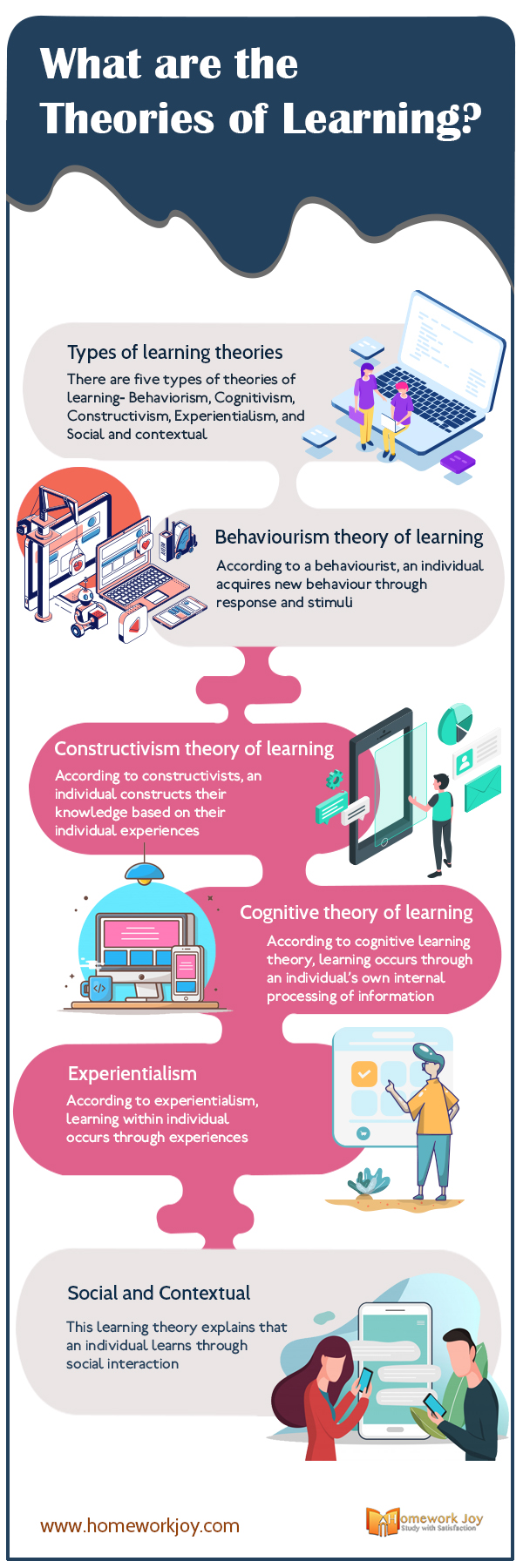
Theories of learning refer to a set of principles that explains how individuals acquire knowledge. By studying theories, we can better understand how learning occurs. The theories of learning are essential for those who want to become teachers, especially.
There are five types of theories of learning:
- Behaviorism
- Cognitivism
- Constructivism
- Experientialism, and
- Social and contextual
Behaviorism
- Behaviorism is a work of B.F Skinner, and he proposed the concept of operant conditioning. Behaviorists believe that learning occurs when a new behavior is acquired through the association between stimuli and response. Behaviorists believe that the learner is a blank state and should be provided with the information.
Cognitivism
- The theory of learning, including cognitivism, is propagated by Jean Piaget. Cognitive theorists believe that learning occurs through the internal processing of information. The focus of behaviorists is what goes inside the learner’s head through mind instead of through observable behavior. Thus the theory of learning involves reorganization of experiences.
Constructivism
- The theory of learning is based on the principle that a child constructs their knowledge through individual experiences and prior knowledge. The learners construct knowledge, and everyone has a different set of skills.
Experientialism
- The experientialism theory of learning states that a child learns through experiences. The method was propagated by David Kolb, who was influenced by the work of Jean Piaget.
Social and Contextual
- According to the social theory of learning, an individual learns through observation. Learning in an individual occurs through social interaction, and it can take place at any time. The primary source of socialization for a child is family, and next comes the school.
Therefore, theories of learning are essential to study to know about child behavior. It depicts how a child gains knowledge about the world and the way they behave.